Q1. Find the password strength.
For each substring of the password which contains at least one vowel and one consonant, its strength goes up by 1.
vowels={'a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'}, and rest of letters are all consonant.
(Only lower alphabet letters)
Economy Mart is a very popular e-commerce platform because they display the cheapest items first. Economy Mart has decided to migrate its database to Amazon's cloud platform. The product listings in the old database are being migrated into the Amazon database. Customers that go onto Amazon.com will be viewing items from the new database.
Economy Mart has an unusual way of displaying items,
If a customer views the first item, they will be shown the cheapest item in the database
If a customer is currently viewing the kth cheapest item, viewing the next item will display the (k+1)th cheapest item.
If multiple items have the same price, they are ordered alphabetically ascending.
There are 2 types of entries:
The first element in the row is “INSERT” followed by the name of the item (String) and its price (String denoting an Integer). This describes an item being added to the database.
The first element in the row is the word “VIEW”. This is when the customer views an item. The other 2 elements in these rows contain "-" that can be ignored. It is guaranteed that at least one item is added to the database when a customer views an item.
Table of entries
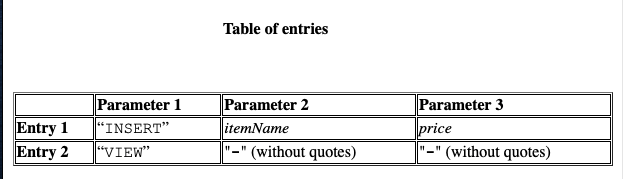
Note: The price of each item is in string format so you may need to convert it to an integer before using it.
While the database is being transferred, an unknowing customer logs onto the website and browses some of Economy Mart's items. Given a server log in chronological order, determine which items were shown to the customer.
Example
entries = [['INSERT', 'milk', '4'], ['INSERT', 'coffee', '3'], ['VIEW', '-', '-'], ['INSERT', 'pizza', '5'], ['INSERT', 'gum', '1'], ['VIEW', '-', '-']]
Let's consider the following entries in the database:
INSERT milk 4
INSERT coffee 3
VIEW - -
INSERT pizza 5
INSERT gum 1
VIEW - -
In this case, milk and coffee are added to the database at costs of 4 and 3, respectively. When the customer logs onto the site, the cheapest item in the database is shown: coffee.
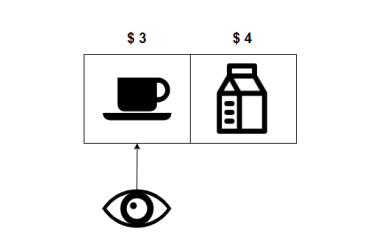
While the customer is browsing, pizza and gum are added to the database. Pizza is worth 5 and gum is worth 1. When the customer views the next cheapest item, the items in the database in sorted order are gum (1), coffee (3), milk (4), and pizza (5). Since the customer is viewing for the second time, the second cheapest item, coffee, will be shown again.
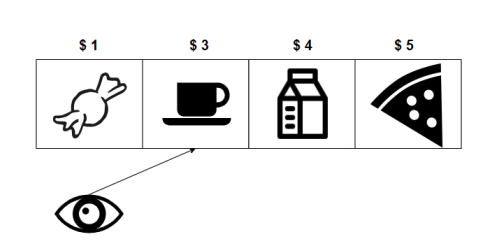
Return ['coffee', 'coffee'].
Function Description
Complete the function getItems in the editor below.
getItems has the following parameters:
string entries[n][3]: each row in the matrix represents an individual log entry
Returns
string[]: answers to each of the "VIEW" queries
Constraints
1 ≤ n ≤ 105
1 ≤ | itemName | ≤ 10 (The name of each item will be 1 to 10 characters long)
Item names will only consist of lowercase English letters.
All itemName strings are distinct
1 ≤ price ≤ 109
k ≤ length of the database (That is, there will always be at least k items in the database when the customer is viewing for the kth time)
Input Format For Custom Testing
The first line of input contains n, the number of entries in the log.
The second line contains the number 3, the size of each entry.
The following n lines each contain an entry with 3 space-separated values.
Sample Case 0
Sample Input For Custom Testing
STDIN FUNCTION
10 → entries[][] size n = 10
3 → entries[n][] columns = 3
INSERT fries 4 → rows of entries
INSERT soda 2
VIEW - -
VIEW - -
INSERT hamburger 5
VIEW - -
INSERT nuggets 4
INSERT cookie 1
VIEW - -
VIEW - -
Sample Output
soda
fries
hamburger
nuggets
hamburger
Explanation
Add 'fries' for 4. db = ['fries'] (costs = [4])
Add 'soda' for 2. db = ['soda', 'fries'] (costs = [2, 4])
For the first "VIEW", the cheapest item in the database, soda, is shown.
For the second "VIEW", the second cheapest item in the database, fries, is shown.
Add 'hamburger' for 5. db = ['soda', 'fries', 'hamburger'] (costs = [2, 4, 5])
For the third 'VIEW", the third cheapest item is shown: hamburger.
Add 'nuggets' for 4, the same price as 'fries'. Sort nuggets and fries alphabetically. db = ['soda', 'fries', 'nuggets', 'hamburger'] ( costs = [2, 4, 4, 5])
Add 'cookie' for 1. db = ['cookie', 'soda', 'fries', 'nuggets', 'hamburger'] ( costs = [1, 2, 4, 4, 5])
For the fourth "VIEW", the fourth cheapest item is nuggets.
For the fifth "VIEW", the fifth cheapest item is hamburger.
Sample Case 1
Sample Input For Custom Testing
STDIN FUNCTION
9 → entries[][] size n = 9
3 → entries[n][] columns = 3
INSERT ruler 4 → rows of entries
VIEW - -
INSERT notecards 2
VIEW - -
INSERT notebook 9
INSERT backpack 10
INSERT pens 6
INSERT pencils 5
VIEW - -
Sample Output
ruler
ruler
pencils
Explanation
First, ruler, worth 4, is added to the database. The database contains ruler = 4.
Next, the customer views the database for the first time. The cheapest item in the database is ruler.
notecards is added to the database and is worth 2. The database contains notecards = 2 and ruler = 4.
The customer decides to view the next cheapest item. After the first item, he is shown the second cheapest item in the database, ruler.
notebook is added to the database and is worth 9. The database contains notecards = 2, ruler = 4, and notebook = 9.
backpack is added to the database and is worth 10. The database contains notecards = 2, ruler = 4, notebook = 9, and backpack = 10.
pens is added to the database and is worth 6. The database contains notecards = 2, ruler = 4, pens = 6, notebook = 9, and backpack = 10.
pencils is added to the database and is worth 5. The database contains notecards = 2, ruler = 4, pencils = 5, pens = 6, notebook = 9, and backpack = 10.
For the third and last viewing, the third cheapest item is pencils.